
Getting the kernel working was an important early first step, but there are many more drivers.
PUTTING LINUX ON A MAC MAC
This allows the kernel to boot natively on the chip that powers the 2020 MacBook Air, Mac mini, and 2021 iMac. Of course you could also generate the appropriate command in other ways, especially if your $PWD isn't currently where that bin directory is. In June 2021 support for Apple’s M1 chip was added to the official Linux kernel. One way you might accomplish this would be to do something like this: : $ echo "export PATH=\"\$PATH:$PWD/bin\""Īnd then copy/paste the resulting line into the appropriate configuration file. depending on your shell), and without reference to $PWD, but rather to whatever it expanded to.
PUTTING LINUX ON A MAC HOW TO
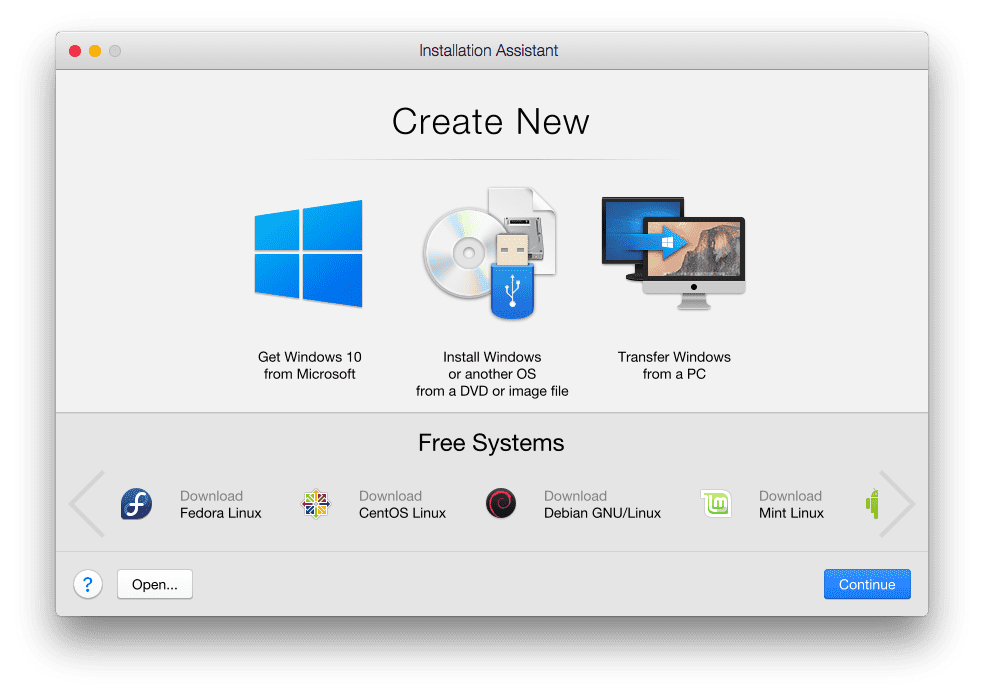
How to get Ubuntu 18.04 (Linux) on a Mac. Presumably, though, you'll want to save this to a shell-specific configuration file (could be ~/.profile, ~/.bashrc, ~/.zshrc. Heres the command to force something to run with the egpu, just put this on the line before the application.

(I won't bother explaining for CSH-compatible shells (because: I agree with other advice that you don't use them), but something similar can be done in them, as well, if that happens to be your environment of choice for some reason.) In just about all but an actual Bourne shell, this can be shortened to: : $ export PATH="$PATH:$PWD/bin" How to do this depends a bit on which shell you're using, but for most ( Bourne-compatible) shells, you should be able to do something like this, if you're in the directory where that bin directory is: : $ PATH="$PATH:$PWD/bin" export PATH So that's the concept, per your question.įrom there, what this documentation is telling you to do is to add the directory where you've unpacked the software, and in particular its bin subdirectory, into your $PATH variable. This is a colon( :)-separated list of directories in which to search for executable files (things like ls, et cetera.) In short, when you try to execute a command from your shell (or from within some other program in certain ways), it will search through each of the directories in this list, in order, looking for an executable file of the name you're provided, and run the first one it finds. (Note: the : $ is meant to represent your shell prompt it may be something very different for you just know that whatever your prompt is, that's what I'm representing with that string.)ĭepending on your system and prior configuration, the value will vary, but a very simple example of the output might be something like: /usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/bin You can find out what your current PATH is set to with a simple shell command: : $ echo $PATH There's a somewhat terse explanation on wikipedia, but basically it's used to define where to search for executable files (whether binaries, shell scripts, whatever). GNU/Linux) systems, which is frequently used and manipulated by the shell (though other things can use it, as well).
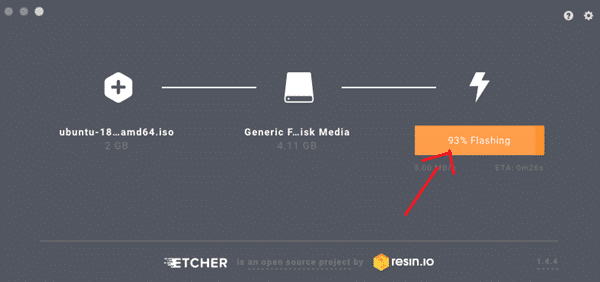
PATH is a special environment variable in UNIX (and UNIX-like, e.g. Here are some great tools I have come across for when you want to create Live or persistent USB Linux distros.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
